|
|||
Particle-laden Flows
Particle-dispersion
Evaporating Sprays
Finite-size Effects
Secondary Breakup
PW Combustors
Stage 35 Compressor
Serpentine Flow
Evaporating SpraysSimulation of evaporating isopropyl alcohol in a coaxial combustor corresponding to the experimental setup of Sommerfeld and Qiu (1998) is performed. Hot air enters the chamber through the annulus, while isopropyl alcohol droplets are injected through the central region. Inflow conditions for spray are based on measured size-velocity correlations at the inlet section. The predictions of mass-flow rates, droplet-size distributions, mean and rms velocities for both phases are in good agreement with the experimental data. 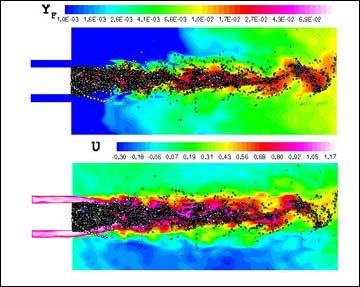
Mahesh, K., Constantinescu, G., Apte, S.V., Moin, P., “LES of gas-turbine combustors,” Annual Research Briefs, Center for Turbulence Research, 2001. Apte, S.V., Mahesh, K., and Moin, P., “LES of evaporating spray in a coaxial-jet combustor,” Comb. Flame, (to be submitted). |


