- HOME
- RESEARCH
- PUBLICATIONS
- PATENTS
- CONTACT
Dysfunctional Innate Immunity Responses
The Barron lab is focused on studying biophysical mechanisms of host defense peptides (a.k.a. antimicrobial peptides) and their peptoid mimics; also, the molecular and cellular biophysics of human innate immune responses.
According to our recent findings, dysfunctional innate immune responses in humans and other mammals involving infection-, injury-, or stress-related dynamic imbalances between particular, potently cytotoxic host defense peptides we study, and pro-amyloid / fibrillogenic peptides including ABeta and IAPP, may play a role in the poorly understood etiology of chronic / progressive plaque diseases, including psoriasis, lupus erythematosus, diabetes type II melittus, atherosclerosis, and particularly, Alzheimers Disease. All of these diseases involve inflammation, dystrophic/senescent cells, and proteopathies with plaque accumulation.
The latter disease, Alzheimers, is in need of a major breakthrough in fundamental understanding, more than almost any human disease currently under study. Of a total of 400+ clinical trials initiated by big pharma towards the development of anti-Alzheimers drugs in the last 14 years, 99.7% of these trials have failed utterly. There is no current effective treatment. Obviously, the most fundamental ideas for what drives Alzheimers must be flawed.
Until recently Alzheimers disease was believed to be the sixth leading cause of death in the United States, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). But in March 2014, research published in Neurology suggested that Alzheimers may actually be responsible for as many deaths each year as heart disease or cancer – the two leading causes of death in the U.S. – due to issues in hospitals of improper prior determinations of underlying cause of death in the elderly.
Natural Killer Cells
Natural Killer Cells
Alzheimers etiology
My lab is testing novel mechanistic hypotheses of Alzheimers etiology, based on our unique molecular biophysical observations of pro-amyloid and innate immune peptides.
Increasing numbers of epidemiological and co-morbidity studies indicate that multiple, progressive degenerative diseases, all involving plaque deposition in various body compartments, are linked. For instance, many researchers have begun to refer to Alzheimers Disease as "Diabetes Melittus Type III". We seek, with current projects, to sleuth out the shared innate immune and molecular biophysical bases for these emerging linkages.
(Note: Succinct, exemplary summaries of these fascinating epidemiological / comorbidity linkages are found, for instance, in the following papers: "The ‘psoriatic march’: a concept of how severe psoriasis may drive cardiovascular comorbidity" Experimental Dermatology (2011) 20, 303–307; "Circle of Willis atherosclerosis: association with Alzheimer’s disease, neuritic plaques and neurofibrillary tangles", Acta Neuropathol (2007) 113:13–21; "Increased prevalence of the metabolic syndrome in patients with moderate to severe psoriasis", Arch Dermatol Res (2006) 298:321–328; "Association of Alzheimer disease pathology with abnormal lipid metabolism", Neurology (2011) 77;1068).
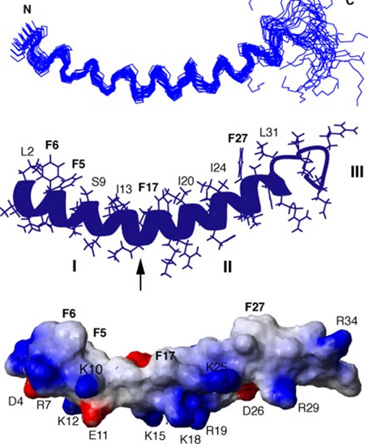
Figure: Human host defense peptide LL-37 NMR structure solved in D8PG micelles
(composed of 37 amino acids)
Research by: G. Wang, J. Biol. Chem. (2008) Vol. 283, No. 47, pp. 32637-32643.