Finding and Verifying CAS Registry Numbers® on STN®
— March 1993 —
Searching with a Registry Number
Here is the basic strategy for: 1) verifying that a Registry Number you have for a chemical substance is truly the correct CAS Registry Number for that substance, or 2) finding the associated substance information for a Registry Number.
- STEP 1 — PREPARE THE NUMBER — write out each number you wish to search.
- STEP 2 — LOG ON TO STN — see the STN Login Card for details.
- STEP 3 — USE THE FILE COMMAND — to enter the Registry File: => FILE REGISTRY
- STEP 4 — DISPLAY the Registry Number record: => D ACC 42228-92-2
- STEP 4.1 — Other Registry Number Fields
- STEP 5 — VERIFY THE ANSWER.
For each number, follow Steps 1, 4, and 5.
STEP 1 — Prepare the Number
Prepare EXACTLY what Registry Number you will search before logging on to STN. Make sure it is in the right format, NNNNNN-NN-N (2-6 digits, hyphen, 2 digits, hyphen, 1 digit).
STEP 2 — Log on to STN
Use the STN Login Card or see Appendix 1 — Logon Procedures for details on Direct Dial procedures.
STEP 3 — Use the FILE Command
Access the REGISTRY File with => FILE REGISTRY
Or, for practice, use the LREGISTRY learning file with => FILE LREGISTRY
STEP 4 — DISPLAY the Registry Number (Accession Number) Record
You may use DISPLAY to view the record for a specific Registry Number without having to EXPAND and SEARCH. Type:
=> D ACC Registry Number
The “ACC” stands for “Accession Number.” Each STN file has an accession number field that uniquely identifies each record in the file. Accession numbers are also called file keys. The accession number for the REGISTRY File is the Registry Number. DISPLAY ACC shows a record in the IDE (substance identification) display format.
=> D ACC 88-14-2 ANSWER 1 COPYRIGHT 1993 ACS RN 88-14-2 REGISTRY CN 2-Furancarboxylic acid (9CI) (CA INDEX NAME) OTHER CA INDEX NAMES: CN 2-Furoic acid (7CI, 8CI) OTHER NAMES: CN .alpha.-Furancarboxylic acid CN .alpha.-Furoic acid CN 2-Carboxyfuran CN Pyromucic acid FS 3D CONCORD MF C5 H4 O3 CI COM LC ANABSTR, BEILSTEIN, BIOSIS, CA, CAOLD, CAPREVIEWS, CASREACT, CHEMLIST, CJACS, CSCHEM, CSNB, DSL, EINECS, EMBASE, GMELIN, HODOC, IFICDB, IFIPAT, IFIUDB, MEDLINE, NAPRALERT, RTECS, SPECINFO, TSCA
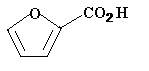
1 REFERENCES IN FILE CAPREVIEWS 568 REFERENCES IN FILE CA (1967 TO DATE) REFERENCES IN FILE CAOLD (PRIOR TO 1967)
Displaying a Registry Number record does not guarantee that it truly is the correct Registry Number for your substance. You still need to verify the record.
You may get an error message indicating your number “IS NOT A VALID ACCESSION NUMBER.” If it is a valid number, it will be on the file. If it is not on the file, then it is not truly a Registry Number.
=> D ACC 93541-34-8 ‘93541-34-8’ IS NOT A VALID ACCESSION NUMBER
The number entered is not a valid accession number in this file. Enter “HELP ACCESSION” at an arrow prompt (=>) for a list of valid accession number formats in the current file.
You may have made a typographical error. Perhaps you omitted a digit or typed an incorrect digit. The number may not be in the correct format of NNNNNN-NN-N (2-6 digits, a hyphen, 2 digits, a hyphen, 1 digit). You may have been given an incorrect number. There are other sources or lists of CAS Registry Numbers besides those available through Chemical Abstract Service, the official source for CAS Registry Numbers. These unofficial sources may be inaccurate.
Even though you did not find the Registry Number you were looking for, do not give up. If you have a chemical name, you can use it to find the substance record and its Registry Number. Details for this are described in the previous section of this booklet, SEARCHING WITH A NAME.
If this approach does not work, consider using CAS Registry Services. For more information, see Appendix 5 — Additional Support.
4.1 Other Registry Number Fields
- Deleted Registry Number
- Replacing Registry Numbers
- Preferred Registry Number
- Alternate Registry Number
An answer may contain other Registry Number fields: Deleted Registry Number (DR), Replacing Registry Number (RR), Alternate Registry Number (AR), and Preferred Registry Number (PR). Their definitions follow.
A. Deleted Registry Number — A Registry Number assigned to a substance but later changed to another Registry Number. The record for this deleted number contains only the replacing Registry Number, RR. All of the substance information is contained in the replacing Registry Number record. The deleted Registry Number displays in the replacing Registry Number record in the DR display field. Examples of substances that are deleted include trade names that appear in the literature with no structural information but are later elucidated to a registered substance.
B. Replacing Registry Number — The Registry Number for a substance. Other Registry Numbers have been deleted to this number. These deleted Registry Numbers display in the DR display field. This Registry Number displays in the RR field for the deleted Registry Number record.
C. Preferred Registry Number — The Registry Number assigned to the more preferred structure of a substance that has more than one structural representation. The Registry Number of the alternate structure appears in the AR display field. The preferred Registry Number displays in the PR display field of the substance record of the alternate structure.
D. Alternate Registry Number — A second Registry Number generated for a second structural representation of a substance. These records have a more preferred structure that is the structure usually encountered in the literature. The record of this less preferred structure will have the Registry Number of the more preferred substance in the PR display field. The record of the preferred substance has the Registry Number searched as if it were an RN. Examples of substances that have AR’s include fluorescein dyes which have the spiro form as the preferred registration and the closed form as the alternate registration.
All of these Registry Numbers are searched when SEARCH NNNNNN-NN-N/RN or DISPLAY ACC is specified. If you SEARCH with a Deleted Registry Number, the Replacing Registry Number record is automatically located. If you SEARCH with an Alternate Registry Number, the Preferred Registry Number record is automatically located. If you DISPLAY ACC on a Deleted Registry Number, its record contains only the Deleted Registry Number in the RN field and the Replacing Registry Number in the RR field.
In the following example, a DISPLAY ACC of the Deleted Registry Number, 83541-34-8, shows it in the RN field and the Replacing Registry Number, 66584-72-3, in the RR field. To view the substance record, you need to DISPLAY ACC on the Replacing Registry Number. The displayed record will have the Deleted Registry Number in the DR field.
=> D ACC 83541-34-8 ANSWER l COPYRIGHT 1993 ACS RN 83541-34-8 REGISTRY RR 66584-72-3 0 REFERENCES IN FILE CA (1967 TO DATE) => D ACC 66584-72-3 ANSWER 1 COPYRIGHT 1993 ACS RN 66584-72-3 REGISTRY CN Maytansine, 2ʹ-de(acetylmethylamlno)-2ʹ-methyl- (9CI) (CA INDEX NAME) OTHER CA INDEX NAMES: CN 4,24-Dioxa-9,22-diazatetracyclo[19.3.1.110,14.03,5]hexacosane, maytansine deriv. (9CI) OTHER NAMES: CN Ansamitocin P 3 CN Ansamitosin P 3 CN Antibiotic C 15003P3 CN Maytansinol isobutyrate DR 83541-34-8 MF C32 H43 Cl N2 O9 LC BEILSTEIN, BIOSIS, CA, CJACS, EMBASE, IFICDB, IFIPAT, IFIUDB, NAPRALERT, RTECS . . .
STEP 5 - Verify the Answer
Even though you have found and displayed a REGISTRY File record, this does not mean you have found the correct record and Registry Number for your substance. Ultimately, you are responsible for determining this or getting help when you need it. Please refer to the last section, Details on Verifying the Answer. See Appendix 2 for logoff instructions.