|
|||
RANS
LES
Integration
Merrimac
Research ProjectsSimulation Framework | Software Engineering | Physics Modeling | Verification & ValidationSoftware Engineering
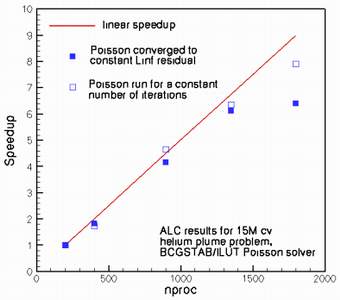
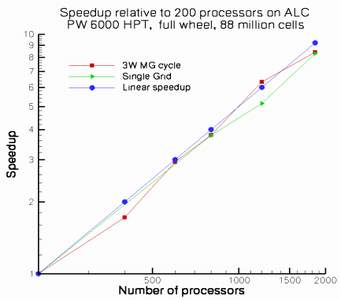
Scalability has been extensively pursued at the Center. Tests have been performed on several platforms; dedicated ALC runs (1,800 CPUs) have demonstrated nearly perfect scalability for TFLO. CDP demonstrated good scalability to 1350 processors. Code I/O has also received considerable attention; both CDP and TFLO use native MPI I/O procedures and have demonstrated I/O rates of 150Mb/sec or greater on a variety of problem sizes. TFLO now uses SubArray types to avoid multiple small requests when writing blocks, and demonstrated writing at 150 MB/s on ALC. In CDP, after preprocessing, refinement or load-balancing, a new set of restart files must be written based on the data on several processors. CDP uses a coloring algorithm to produce sub-communicators, and then collective writes from Indexed type On the streaming side, a new hierarchical programming language that makes it significantly easier to develop applications for exposed-communication architectures has been developed. Also a detailed architectural design of a stream processor was completed. |