|
| Home |
People | Projects | Publications |
Places |
Products
The Federal Technology Transfer Act of 1986 promotes
commercialization of government research. Through technology transfer efforts,
Rehabilitation R&D Center projects become products that can be purchased
for the benefit of veterans with disabilities. Below are brief descriptions and
the commercial status of products which were developed at the Rehab R&D
Center and have been brought to market. This information does not constitute an
endorsement by the VA.
Automatic Decomposition Electromyography
ADEMG
(Automatic Decomposition Electromyography) is a computer program for analyzing
clinical electromyograms which was developed at the Stanford Department of
Neurology and the Rehab R&D Center. The program analyzes EMG signals by
decomposing them into trains of motor-unit action potentials and then measuring
the properties of those potentials. In 1988, a commercial version of ADEMG was
released by Nicolet Biomedical Instruments, Madison, WI, to run on the Nicolet
Viking electromyograph. At that time, ADEMG was the only commercial program
able to decompose EMGs recorded during moderately forceful contractions, and it
continues to be one of the premier programs in this regard. Over 100 copies of
the ADEMG program have been purchased by researchers and clinicians throughout
the world. For further information, contact:
Nicolet Biomedical
Instruments
5225-4 Verona Rd.
P.O. Box 4287
Madison,
WI 53711
800/356-0007

Alexis Wheelchair
Alexis is an innovative
electric wheelchair using a "wheels within wheels" design. It is unique in that
it can turn in its own footprint and move sideways. The Rehab R&D Center
licensed Intex Industries to make Alexis commercially available in 1987, and
Intex made 40 pre-production units for field trials in the San Antonio area.
During subsequent redesign efforts, the company filed for bankruptcy,
preventing further commercialization at this time. |
|

Arroya Ski-sled
The Arroya is a ski-sledding
alternative to downhill skiing for people with physical disabilities. The
Arroya is an aerodynamically contoured, reinforced fiberglass shell with metal
runners for steering and turning control, and is accommodated on ski lifts.
Many units have been sold and used internationally for both pleasure and
para-olympic competition. Although the Arroya is no longer manufactured, it has
inspired the development of similar sit-ski designs, and other enhancements of
winter sports equipment. It was made commercially available by:
Beneficial
Designs |
Distribution of Conduction Velocities
A research
project in the early 1980's at the Stanford Department of Neurology and the
Rehab R&D Center lead to the development of a method for estimating the
distribution of conduction velocities (DCV) of the fibers in a peripheral
nerve. DCV analysis is more sensitive than conventional nerve-conduction
measurements since it characterizes the velocities of all the large myelinated
fibers in the nerve bundle instead of just the fastest ones. A software program
for DCV analysis was developed for the Pathfinder evoked-potential machine
produced by Nicolet Biomedical
Instruments, Madison, WI.
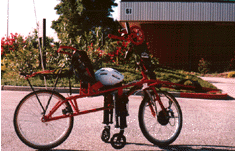 Handbike Handbike
The arm-powered Handbike is a true
two-wheeled bicycle specifically designed for people with lower limb
disability, such as paraplegia or amputation. Riders experience the
exhilaration of quick accelerations, speed, and leaning into curves as they
power, steer, and brake with the hand cranks. Suspended side casters touch down
at a pre-set maximum lean and latch for four-wheeling, transfering, ascending
ramps, and maneuvering in tight situations. Riders with limited trunk stability
balance the Handbike by steering. A folding crank tower option facilitates
transfers. The Handbike began as a student project in the Stanford Design
Division of Mechanical Engineering with further development at Rehab R&D
Center under sponsorship from the Telephone Pioneers of America and the British
Columbia Program for the International Year of the Disabled Person. It is
commercially available. For further information, contact:
New Dimensions Design
90127 W. Demming Rd.
Elmira,
OR 97437
503/935-3162
503/343-7037 fax
|

HandTyper
The HandTyper is a simple and
effective typing aid that is commercially available and has been popular with
occupational therapists and patients. For people with spinal cord injury and
others with limited hand function, it provides a way for the user to type, turn
pages, and move paper on desks. It offers a secure fit, gives visual access to
keyboards, and is padded to protect the dorsal suface of the hand. For further
information, contact:
Alimed, Inc.
297 High St.
Dedham, MA 02026-9135
800/225-2610
|
|

Lingraphica
Lingraphica is a portable
assistive and therapeutic communication device for people with aphasia from
stroke or other brain injury. It was developed under a Merit Review project at
the Rehab R&D Center in 1987-1989 and commercialized in 1990 under the
Technology Transfer Act. In 1996, the parent company, Lingraphicare America,
redirected its efforts from selling medical devices to providing clinical
language and speech therapy services to adults with aphasia. Their services
employing Lingraphica report greater rates of improvement and better ultimate
outcomes than traditional speech-language therapy.
Journal article:
Improving
Outcomes for Persons with Aphasia in Advanced Community-Based Treatment
Programs
For information or referral, contact:
LingraphiCARE
America, Inc.
425 Jackson St.
Oakland, CA 94607
510/302-0400
520/302-0500 fax |
|
Software for Interactive Musculoskeletal
Modeling
Software for Interactive Musculoskeletal Modeling (SIMM) is a
graphics-based software system that quickly develops and analyzes
musculoskeletal models consisting of a set of rigid body segments connected by
joints. SIMM runs on Silicon Graphics workstations. To date 30 copies have been
sold, including several in Europe and Japan. Musculographics, Inc. is
distributing SIMM, and may be contacted for more information at:
Musculographics, Inc
1840 Oak
Ave.
Evanston, IL 60201
847/866-1882
847/866-1808
fax |
|

Dynamics Pipeline
Developed at the Rehab
R&D Center in the late 1980s, the Dynamics Pipeline is a suite of software
tools that performs forward and inverse dynamic simulations on musculoskeletal
models. It connects SIMM (above) to SD/FAST (Symbolicm Dynamics, Mountain View,
CA) which simulates the dynamics of rigid-body systems. Once a musculoskeletal
model is created in SIMM, Dynamics Pipeline translates it into a model which
SD/FAST can execute to create a complete simulation program. This program
computes dynamic muscle force, torque, and body segment motion. Dynamic
Pipeline runs on Silicon Graphics workstations. It is available from
Musculographics, Inc. For more information contact:
Musculographics, Inc
1840 Oak
Ave.
Evanston, IL 60201
847/866-1882
847/866-1808
fax |
VA-Twist Software
VA-Twist is a software program
for bioengineering applications. It uses finite element methods to calculate
the area and torsional properties of general cross-sectional geometries,
especially cross sections of long bones. It runs on IBM-compatible computers
with Microsoft 32-bit Fortran Power Station, Macintosh computers with Mac
Fortran II and MPW, and most engineering work stations equipped with an ANSI
Fortran compiler. It is available at no charge from:
Gary Beaupre,
PhD
Rehab R&D Center
650/493-5000 ext. 6-4272
650/493-4919
fax
Low Vision Reference
Low Vision Reference is a
database of 6400 citations in the blindness and low vision field. The initial
product was created at the Western Blind Rehabilitation Center and Rehab
R&D Center in 1989. The first two editions have been sold and used in 14
countries. The third edition is now available in print and on disc in DOS and
Macintosh formats. The EndNote citation manager and 81 keywords facilitate
searching and browsing the database. For more information, contact:
Lighthouse Industries
Attn: Publications Department
36-20 Northern Blvd.
Long Island City, NY 11101
800/334-5497
|

Veterans Administration Seat Insert Orthosis
The VASIO (Veterans Administration Seat Insert Orthosis) seat cushion for
wheelchair users was originally developed by the Rehabilitation Engineering
Center at Packard Children's Hospital under contract from the VA Palo Alto
Spinal Cord Injury Service. It was clinically tested at the Spinal Cord Injury
Service, it has been used successfully for many years. Additional information
can be obtained from:
Orthopedic Systems Inc.
30031 Ahern Ave.
Union
City, CA 94587-1234
510/429-1500
510/429-8500 fax
|

|







