Circuit Placement Example
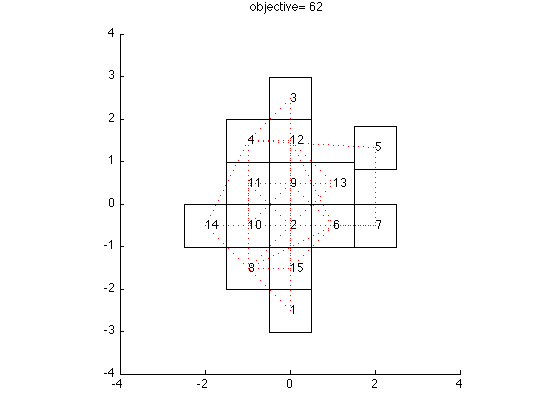
This example uses the convex-concave procedure to solve the problem of placing square circuit components on a chip to reduce the wirelength between them. Details can be found in section 5.3 of Variations and Extension of the Convex-Concave Procedure.
This example uses CVX, which is available here.
You can download the code circuit_placement_example.m, along with the two subroutines random_graph_generator.m and plot_circuits.m.
Contents
clear all close all
Problem generation parameters
rand('state',0); N = 15;% number of components xbound = 4; % symmetric bounds on the bounding box in the x direction ybound = 4; % symmetric bounds on the bounding box in the y direction trials = 1; % number of initialization rho = .4; % the chance any particular edge is in the graph % a matrix with the height and width of each circuit component. Circuits_size = ones(2,N);
Algorithm parameters
embedding_init = 0; % if 1, the first init. will be the Laplacian embedding iterations = 150; % maximum number of iterations Tau_init = 0.2; Tau_inc = 1.1; Tau_max = 1e4;
Laplacian embedding for an Erdos-Renyi random graph
L = random_graph_generator(N,rho); % find the Laplacian embedding if(embedding_init) [V D] = eig(L); i = 1; while(D(i,i) < 1e-8) i = i+1; end x = V(:,i); y = V(:,i+1); x = (x-((max(x)-min(x))/2+min(x)))/(max(x)-min(x)); y = (y+((max(y)-min(y))/2+min(y)))/(max(x)-min(x)); circuits = [2*xbound*x';2*ybound*y']; end
Convex-concave procedure
figure cvx_best = inf; gradients = zeros(N*(N-1)/2,4); constraint_val = zeros(N*(N-1)/2,1); for Initialization = 1:trials %randomly initialize if(~embedding_init || Initialization~=1) circuits = [2*xbound 0; 0 2*ybound] *(rand(2,N)-.5); end %plot initial placement plot_circuits(circuits,Circuits_size,L,xbound,ybound,-1,-1,... Tau_init,Initialization) converge = 0; % flag to ensure two steps without change for convergence cvx_prev = inf; Tau = Tau_init; for k = 1:iterations circuits_c = circuits; % precalculate gradients for i = 1:N-1 for j = i+1:N index = ((N-1)+(N-i+1))*(i-1)/2+j-i; % determine the vertical and horizontal margin on the % constraint. horiz = (Circuits_size(1,i)+Circuits_size(1,j))/2-... abs(circuits_c(1,i)-circuits_c(1,j)); vert =(Circuits_size(2,i)+Circuits_size(2,j))/2-... abs(circuits_c(2,i)-circuits_c(2,j)); %set which subgradient to use if(abs(horiz-vert) < 1e-5) use = mod(k,2); % if the same alterante elseif(horiz < vert) % otherwise, go with the smaller use = 0; else use = 1; end if(use == 0) s = sign(circuits_c(1,i)-circuits_c(1,j)); gradients(index,:) = [-s 0 s 0]; else s = sign(circuits_c(2,i)-circuits_c(2,j)); gradients(index,:) = [0 -s 0 s]; end constraint_val(index) = min(horiz,vert); end end cvx_begin quiet variables circuits(2,N) slack(N*(N-1)/2) %the objective is the wire length between all connected %components. objective = 0; for i = 1:N-1 for j = i+1:N if(L(i,j) < 0) objective = objective + abs(circuits(1,i)-... circuits(1,j)) + abs(circuits(2,i)-circuits(2,j)); end end end minimize objective + Tau*(sum(slack)) subject to %non overlapping constraint. for i = 1:N-1 for j = i+1:N index = ((N-1)+(N-i+1))*(i-1)/2+j-i; constraint_val(index)+gradients(index,:)*... ([circuits(1,i); circuits(2,i); circuits(1,j); circuits(2,j)]-... [circuits_c(1,i); circuits_c(2,i); circuits_c(1,j); circuits_c(2,j)]) <= slack(index); end end slack >= 0; abs(circuits(1,:)) <= xbound-Circuits_size(1,:)./2; abs(circuits(2,:)) <= ybound-Circuits_size(2,:)./2; cvx_end %plot the resulting figure plot_circuits(circuits,Circuits_size,L,xbound,ybound,... objective,sum(slack),Tau,Initialization) if(norm(cvx_prev-cvx_optval) <= 1e-3 &&... (sum(slack) <= 1e-3 || Tau == Tau_max)) if(converge == 1) break; else converge = 1; end else converge = 0; end Tau = min(Tau*Tau_inc,Tau_max); cvx_prev = objective + Tau*(sum(slack)); end if(cvx_optval < cvx_best) cvx_best = cvx_optval; circuits_best = circuits; end end plot_circuits(circuits_best,Circuits_size,L,xbound,ybound,... cvx_best,-1,-1,-1,1)