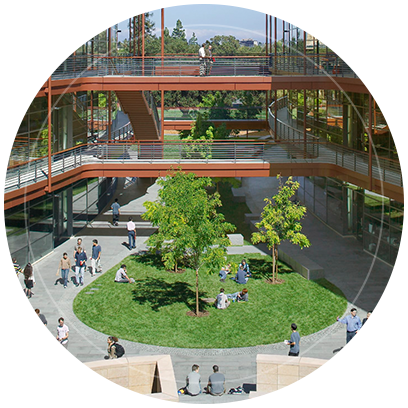
The James H. Clark Center
The iconic form of Clark Center embodies the collaborative spirit of Bio-X. Sweeping windows reveal open lab spaces which dissolve the walls between labs, people and ideas. Researchers flow through this nexus that blends traditional departments, schools and areas of study.
Visit our timeline to explore highlights of the achievements of Bio-X.