CS 101
Computer Science Theory and Conclusions
Announcements
- Final is on Monday, December 10, 8:30AM-11:30AM in 200-203. If you have an exam accommodation and haven't received an email from Shreya, please email both of us.
- Practice final exam materials are posted on the website (same reference sheet as last time)
- Final review session on Thursday! Come with questions
- Please give us EOQ feedback
- Shreya will move her OH from Wednesday to this weekend. Stay tuned!
Plan for Today
Wrap-up of the quarter
- A topic you chose: quantum computing
- My field of study: computer science theory
- Final thoughts
Quantum Computers
- Recall: traditional computers have bits - either 0 or 1
- Superposition allows a qubit to be a combination of 0 and 1. Note: when measuring or looking at a bit, it'll still be 0 or 1. For example, we could set it so that 50% of the time, the qubit is measured as a 1
- Entanglement connects two bits together (so coming out of superposition, entangled bits will always have the same value)
- Interference: can amplify the right answer to increase probability of getting the right answer or destructively decrease the likelihood of following a path to the wrong answer
- Good for simulating nature
- Idea: can simulate many things simultaneously
- Example: break popular encryption schemes
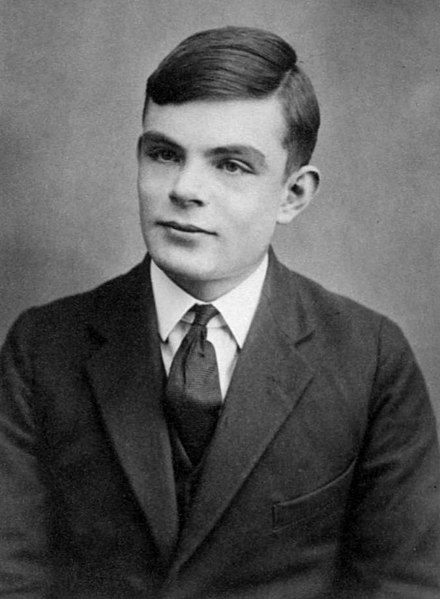
Alan Turing
- Developed the Universal Turing Machine to prove that some problems are unsolvable
- One example: finding the cheapest sequence of flights for a trip
- Another example: we can't tell if a program will ever end
- Broke Enigma encryption
- Turing Test in Artificial Intelligence
- Turing Award ("Nobel Prize of CS") named after him
"Good" Algorithms
- Algorithm: way to solve a problem
- Two main resources: time and space (memory)
- Good algorithms run faster with respect to input size
- Getting the red value of a pixel always takes the same amount of time (constant)
- Studying an exam requires reading every slide (linear)
- Green screen: double the width and height of the image, quadruple the number of pixels to look at (polynomial)
- Listing all the two digit numbers takes one-tenth the time as listing all the three digit numbers (exponential)
Algorithms in practice: Search
- We want to see if a certain value is in a sorted list of elements
- Could look through all the values one by one (linear)
- Binary Search
- Look at the middle value
- Only need to look at the left values if it's too big
- Only need to look at the right values if it's too large
Algorithms in practice: Sorting
- Bogosort: randomly pick all the elements, then check if the list is in order (really, really slow)
- Insertion Sort: Add the elements one-by-one
- Bucket sort: pick categories for the data, then put each item in one of those buckets
- Commonly used with exams
- Idea: faster if we relax our definition of "sorted"
P vs. NP
- Biggest unsolved question in Computer Science (million dollar prize)
- Basic idea: is it just as fast to solve a problem as it is to check that the solution is correct?
- NP: guess a solution (very fast) and check that it's correct
- P: actually find a solution
P=NP: Implications
- Encryption would break
- Much better optimization (everything's faster!)
- Better transportation layouts
Midpoint Recap
- Abstractions can help computer scientists think about problems differently.
- Some problems in computer science don't have any solutions (computers are not all-powerful).
- Some problems don't have any "good" solutions.
- There are lots of ways to solve problems! Computer scientists constantly try to find better ways.
Course Themes
- Technology defines our society
- Understanding technology keeps you safer and more informed
- Lots of different parts of computer science
Our Quarter
- How computers work
- Programming
- AI
- The Internet
- Backend, Frontend, and Human-Computer Interaction
- Security and Privacy
- Theory
Learning Goals
- Improve technical literacy, understanding computer terminology.
- Understand how computer code is written.
- Describe how computers and the internet works behind the scenes.
- Understand the technologies most discussed in the news and how technology affects society.
Thank you
It's a hard course, and you all have done very well. Good luck on the final!