CS 101
Servers and Backend
Announcements
- WiCS Dinner Tonight at Gates 403
Plan for Today
- Recall: requests go to a server, which returns a response
- Today: how do servers figure out what information to return?
- Displaying Ads
Information Storage: Databases
- One strength of computers is their ability to store and process information
- Information is stored in databases
- Like a giant Excel sheet, but with lots of rows
- Usually can't "see" all the data - choose certain columns at a time, or filter out rows with certain features
- Example: I want to send an email to all users in North America who last logged in between 5 and 7 days ago and who have an outstanding friend request
- Basic Idea: companies store a lot of information, then responses involve searching the saved information based on the request
- Come back Thursday!
Power of Data
- Talk with a neighbor: what sorts of data do you think your favorite websites store?
Power of Data
- A good rule of thumb: every click, view, and even mouse hover is recorded and stored
- Tracking this kind of data can be very powerful
- Are people getting frustrated because a video takes too long to load?
- Which articles are the most popular?
- Which genres of movies/TV are most popular? (Netflix is phenomenal at this)
Google: Getting Information
- Indexes the internet
- "Spiders" "crawl" the internet (Google calls them "Googlebots")
- Start on a page, index that page, follow all outbound links
- Store all the information in a database
- Contains info about the words pages contain
Google: Evaluating Relevance
- Request includes search terms
- Need to derive meaning from order of terms (Natural Language Processing)
- Search all the indexed websites
- Look for terms and their synonyms; terms in the title are better
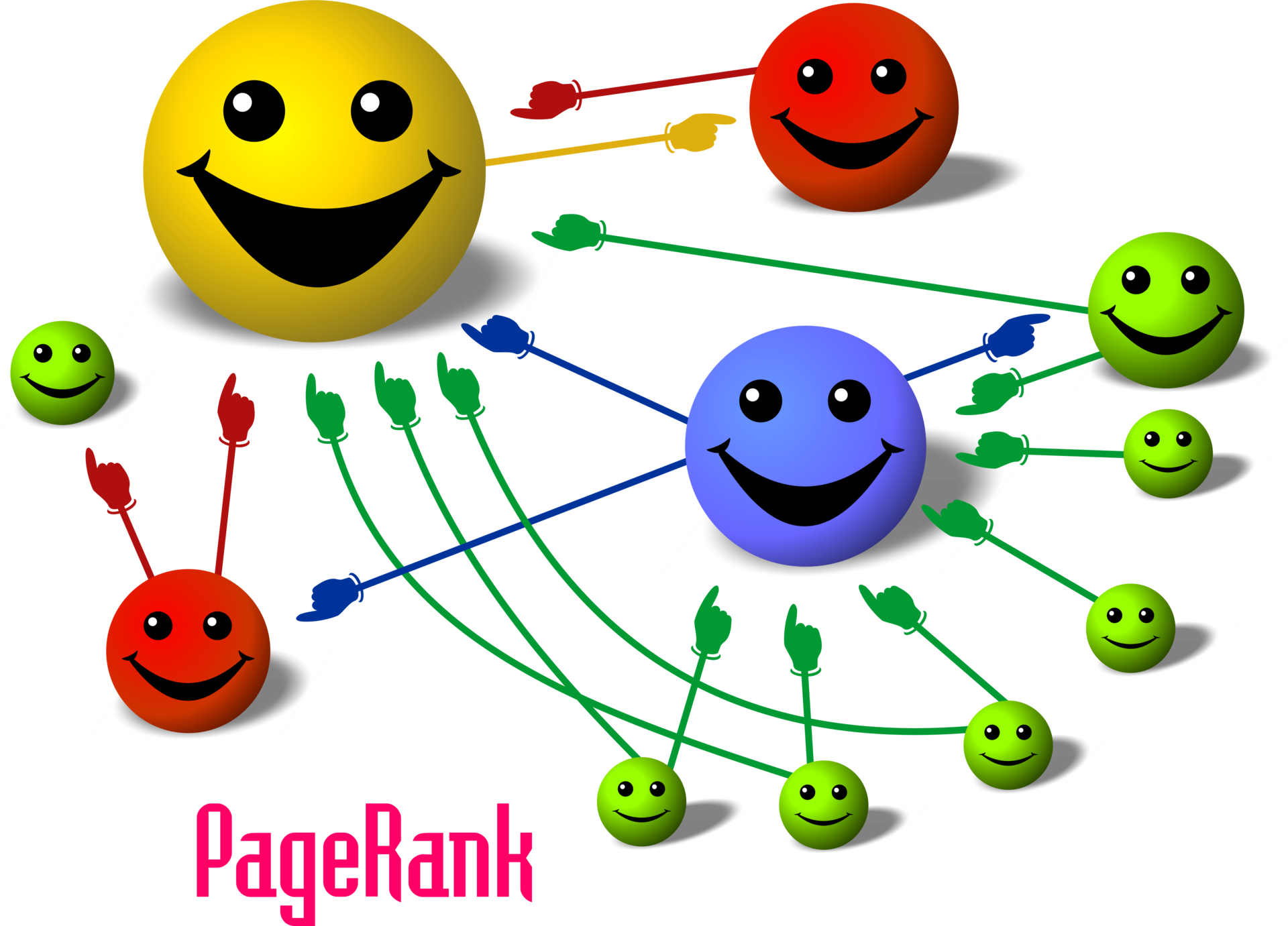
- PageRank: a measure of how "important" a website is
- Sort of like how academic papers work: being cited by lots of papers is better, and being cited by other important papers is better
Google Search: Recap
Facebook: Storing Friends
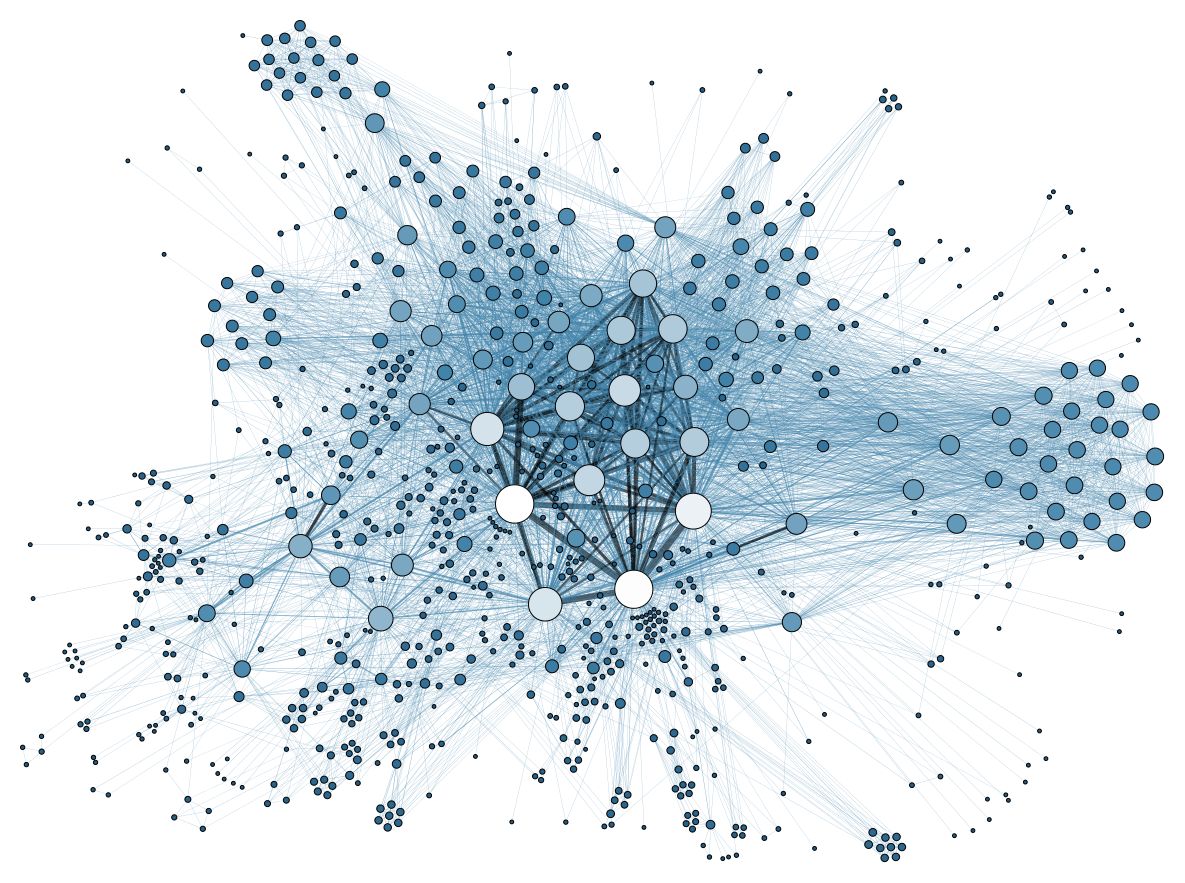
- Social Network: people are connected to each other through friendships
- Called a graph in CS
- nodes = people
- edges = friendships
- Other uses of graphs: the Internet, road networks, disease outbreaks, company hierarchies
Facebook as a Network
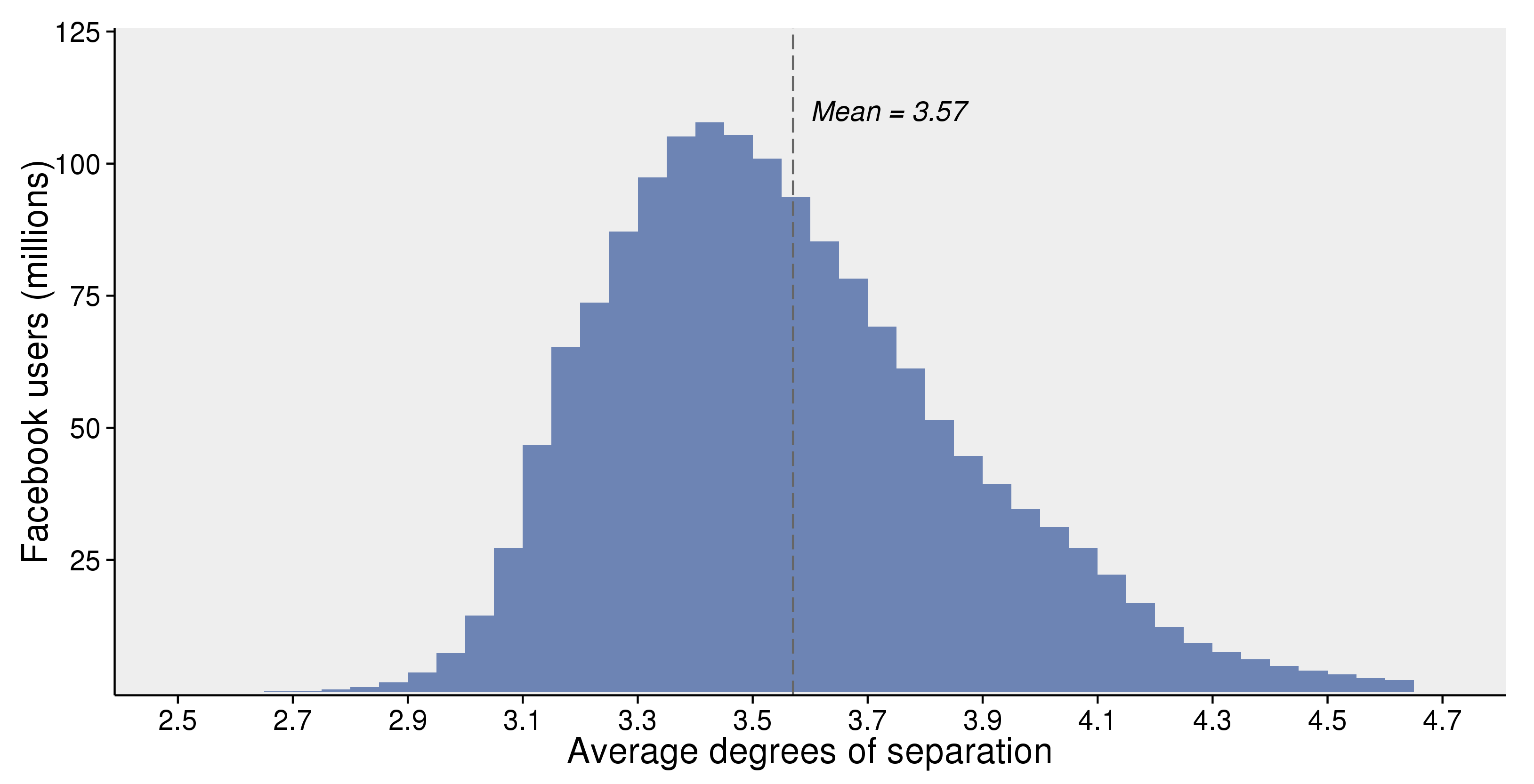
- Friendship Paradox: your friends have more friends on average than you do
- Triadic Closure: how People You May Know works
- Degrees of Separation and (Kevin) Bacon number
Storing Other Information
- Stores likes, comments, posts, live videos, messages, etc.
- Big idea: give IDs to users and each type of interaction
- Tables in a database for each of these, linked by IDs
- News Feed algorithm: get the content from each of your friends, attempt to rank using relevance, popularity, and recentness
Internet Advertisements
- Some target certain types of individuals: Facebook
- Some target certain search terms: Google
- Some track your internet search history through ad-tracking using third-party cookies that are shared across websites
- In general, ad campaigns have a budget and a bid per view or bid per click; ordering on a page and which ads are visible are based on bids
Recap
- Companies decide how to store information
- How companies prioritize information and interpret requests has a huge impact on society
Exam
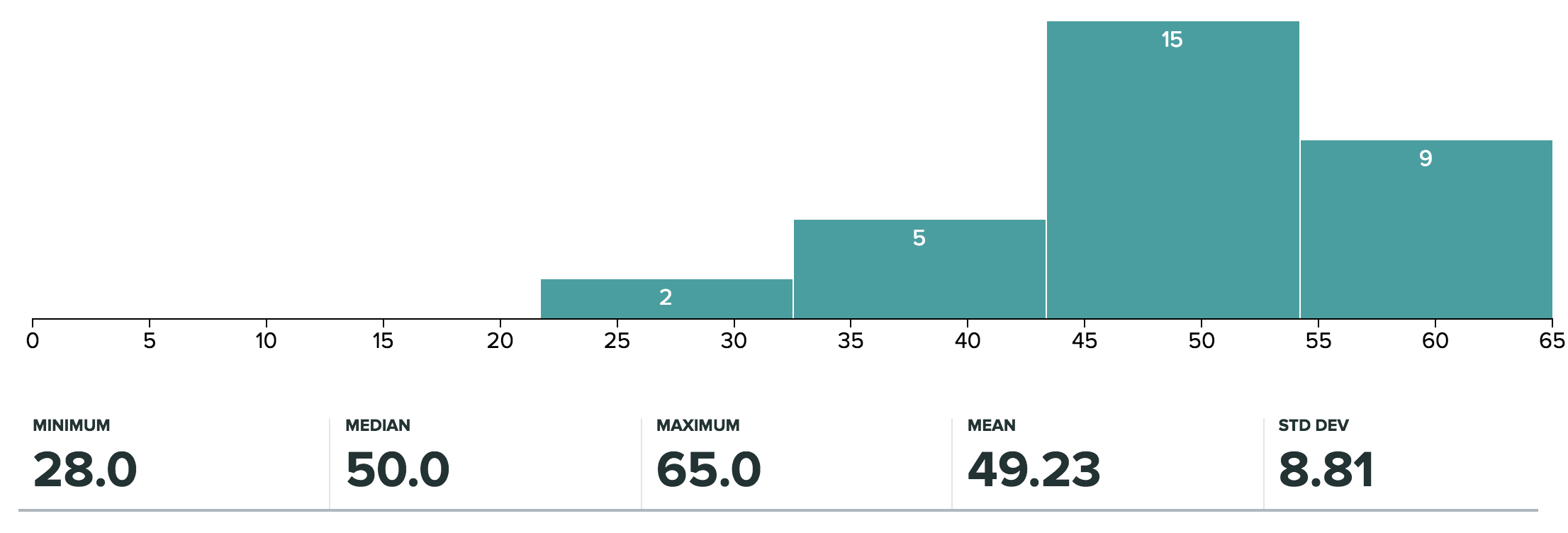
- Great job on the exam!
- I will curve the class similarly to past courses (as viewable on Carta)