CS 101
Artificial Intelligence
Lecture by Shreya Shankar, TA
Announcements
- Midterm is one week from today (Tuesday, October 30) during class in STLC 115. If you have an exam accommodation and haven't received an email from Shreya, please email us.
- Practice midterm on website
- Review session in class Thursday
- No homework on this material, but homework from last week due Wednesday
Plan for Today
- Last week, we saw how we can easily visualize data in spreadsheets.
- Today, we'll see how computers can learn from data in a field called Artificial Intelligence.
- What is AI
- Some AI algorithms
- Branches of AI
- Challenges
AI: A Brief Overview
- Input: data
- Output: model used to make predictions
- Predictions make it seem as if the computer is thinking
- Makes guesses about new data
History of Artificial Intelligence
- Fascination since early humanity of forging intelligence like the gods
- Formal logic in mathematics - mechanically reasoning about math (ancient days through 1920s and 30s)
- 1940s and 50s: "Neural Nets": Try to duplicate the way the human brain works
- 1956: Dartmouth Conference: belief that machines could simulate human thought
- 1987: Deep Blue beats the world chess champion
- 2011: Watson wins at Jeopardy!
- 2012: Image classifiers get really good
- 2014: Deep learning hype builds
Turing Test
- What does it mean to have truly intelligent AI?
- AI: good at performing computationally intensive tasks. Anything we can do with a calculator or do in a couple seconds, AI can do.
- AI: bad at doing things we can easily and passively do, like understand a book or carry a conversation about lots of things.
- Turing test: two participants (one machine and one human), and a human evaluator. Human evaluator has to decide which participant is the machine, and which participant is the computer.
- Trace
Machine Learning
- Algorithms that improve over time with more observations (data)
- Idea: the model will be better/smarter as it is used in the real world
- Basically fancy statistics :)
- Example: Netflix's recommendations become better the more you watch
- Trace
Technique: Linear Regression
- Linear regression: try to predict one variable's value based on other (known) variables
- Idea: make a line "fit" the data, then use the line to make our predictions
- Example: given age and gender, can generally predict height fairly accurately (within a couple inches); as age goes up, height goes up too
Technique: Predict by Grouping
- Idea: sort a new piece of data into the same category as its "nearest neighbors", already categorized data that is similar to the new sample
- You're likely to live in the same country as your three closest friends on Facebook
- Automatically "reading" addresses on envelopes
Natural Language Processing
- Build probability models for language
- Google autocomplete: "guess" the next word
- Chatbots/Siri/Alexa
- Turing Test (The Imitation Game)
- Trace
Computer Vision
- Challenge: extract visual meaning from grid of pixels
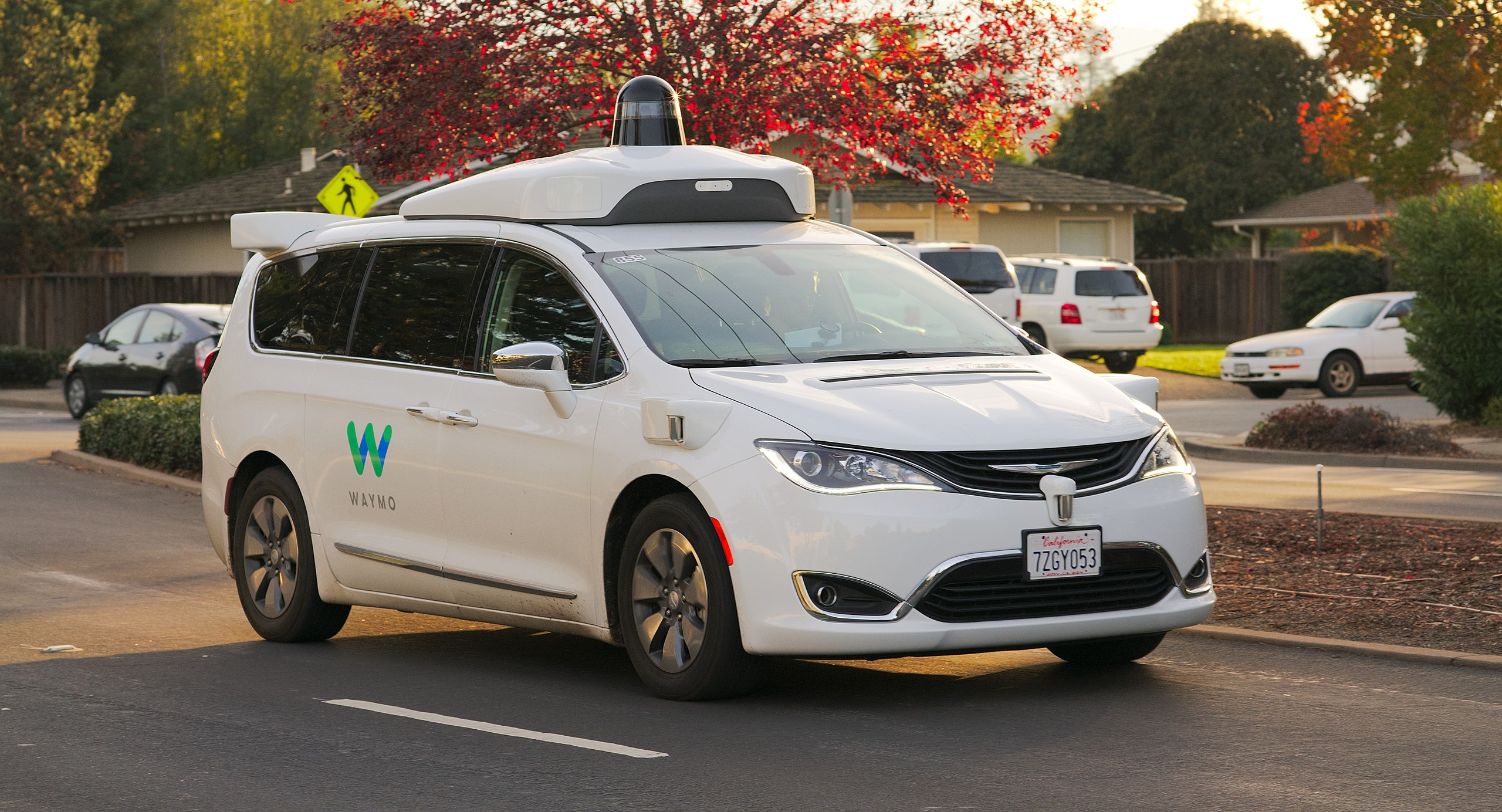
- Self-driving cars (actually supplement with LIDAR)
- Handwriting recognition
- Auto-captioning images on Facebook (for visually impaired)
- Trace
Robotics
- Challenge of incorporating senses and movement
- Prosthetic limbs
- Defusing Bombs
- Trace
Safety
- How do you develop AI that doesn't take over the world?
- AI is a tool. Researchers can't prevent bad people from being bad, but we can prevent AI from acting badly when good people use it.
- Value alignment: align AI systems with our values (Trace)
- Reward hacking: find easy or trivial solutions that weren't intended (Trace)
- Security: AI models are vulnerable to attacks (adversarial patch)
Challenges
- How do we measure "better"?
- Loss of jobs due to automation (similar to Industrial Revolution)
- Machine learning might not be fair (AI detecting toxicity, face recognition bias)
- What checks do we have on AI?
Recap
- AI is all around us and affects our lives in innumerable ways.
- However, we must carefully think about how we can mitigate its negative impacts.